Already available! The weekly World Economic Digest (Wednesday) on 05.08.2023 presents the most significant economic events and their impact on the world economy. In this issue, we will look at the latest updates in world trade, the development of financial markets, changes in the political situation and their possible impact on international firms and investors.
THE LABOR MARKET IN THE US – THE FIGURES ARE BELOW THE FORECAST, WAGES ARE GROWING AT THE SAME PACE
The released BLS statistics on the US labor market for July showed the following indicators (all worse than expected):
• Number of new jobs 187K vs 185K in June (forecast 200K)
• * Private sector: growth by 172K vs 128K, forecast 179K (we consider the dynamics in Private to be a more representative indicator of the situation)
• Unemployment rate: 3.7% vs 3.9% a month earlier, forecast 3.8%
• Salary growth: 0.4%mm and 4.4%yy vs 0.4%mm and 4.4%yy in June. Forecast: 0.3% mm and 4.2% yy
• Participation rate not: 62.6% vs 62.6 a month earlier.
Again, there is a strong dissonance with the previously released figures from ADP (+324K). The growth rate of wages is not decreasing.
Now let’s take a closer look at the labor market:
👨🔧Employment is stabilizing before declining in Q3. Job growth in the US amounted to +187K in July. This is 40% lower than the average for 12 months. At the same time, unemployment remains at 3.5%.
👨⚖️The main engine of employment remains government spending:
🏥+63K healthcare
🧑🦼+24K social assistance
🏦+19K financial markets
🏗️+19K construction
🏕️+17K tourism
Government-related segments account for +87K new jobs (46% of the total increase in July). These are mainly healthcare (the Medicare program), social assistance and infrastructure construction (the Biden plan). In these segments, the growth of seats is ahead of the market average for 12 months.
👨🎓In autumn, seasonality will take construction and tourism out of the market. The costs will be hit by the resumption of payments on student loans in the fall. The total amount of debt owed by 27 million citizens exceeds $1.1 trillion. According to BofA, in the 2nd half of the year, the delay will return to 11% ($167 billion). According to Morgan Stanley, 90% of the funds for payments will be transferred from current consumption. This is equivalent to a loss of more than 0.1% of GDP growth.
In general, the labor market report does not change the current situation for the Fed: the labor market is quite hot, there are a lot of vacancies, applications for benefits and the unemployment rate are low, wages are growing faster than the Fed wants to see… but employment growth is slowing down. The labor market is on a trajectory even better than the Fed’s current forecast (4.1% unemployment at the end of the year and another increase after a pause).
USA: QT continues, but Yellen helps
The Fed is gradually continuing to reduce the balance sheet, the securities portfolio has decreased by $33 billion in a week, by $79 billion in the last 4 weeks, the total balance has been reduced by $97 billion in 4 weeks due to the repayment of part of the FDIC loans to $8.2 trillion.
However, this time the US Treasury, which had quite large expenses at the beginning of the month, spent $89 billion from its accounts with the Fed, reducing the amount of funds for them to $461 billion, because there were even more dollars in the system. Given that at the end of the 3rd quarter, the US Treasury wants to have $ 650 billion in the account, and at the end of the year $750 billion – it will withdraw liquidity from the system by the end of the year, the Fed plans to do the same.
At the same time, the US Treasury will have to finance a high budget deficit and plans net market borrowings in the 3rd quarter of $ 1 trillion, of which $178 billion in bonds, and the rest in promissory notes for up to a year, and in the 4th quarter Yellen wants to borrow $0.85 trillion, of which already $339 bonds, taking into account loans in July it is necessary to borrow another $1.5 trillion of net loans, of which about 2/3 are promissory notes and 1/3 are bonds. The pressure on the debt market may increase even more, especially after the psychological action in the form of a downgrade, which makes the market think a little more about the sustainability of the US budget.
Against this background, the debt curve is slowly growing – long securities have reached 4.2-4.3%, i.e. +0.6 pp by the time the debt ceiling is raised. The outflow of liquidity will continue until the end of the year (the Fed and the US Treasury plan to withdraw ~ $0.8 trillion), but it can be significantly offset by a reduction in reverse repo. For the debt market, the situation potentially looks even worse than could be expected, since Yellen’s main loans are still ahead this year….
#USA #inflation #economy #Fed #debt #rates #dollar
Global Investors Switch from China’s Flag to India and Vietnam
Global capital flows are shifting away from China in favor of other emerging Asian markets such as India and Vietnam as investors seek alternatives with less economic and geopolitical risks.
❗️ For the first time since 2017, the inflow of foreign investment in Asian emerging market stocks, excluding China, over the past year exceeded the net purchase of mainland Chinese stocks through the Stock Connect program. According to Goldman Sachs, these amounts amounted to $39 and $32 billion, respectively.
This is due to the fact that investment funds specifically designed for non-Chinese economies are emerging at a record pace.
“Foreign purchases have grown strongly in the region outside of China” over the past four months, writes Sunil Cole, Goldman’s Asia-Pacific equity strategist.
China’s economy is experiencing an unexpectedly slow recovery after the pandemic, hampered by a downturn in the real estate market and high youth unemployment. But sluggish growth is not the only problem.
Hiroshi Matsumoto, senior researcher at Pictet Asset Management (Japan), says that American and European investors are concerned about the consequences of a potential Taiwan conflict. “There are concerns that assets may be frozen or otherwise it will be difficult to sell them, as happened with Russia after the start of the SVO,” he said. “Investing directly in mainland Chinese stocks is risky.”
This is in addition to ongoing concerns about human rights in China.
Investors gravitate towards India as an alternative destination. Having risen since April, the benchmark Sensex index is now hovering in record territory. In 2023, a total of $12.8 billion of foreign capital was invested in Indian stocks, ahead of Taiwan and South Korea, despite the fact that their markets support semiconductors.
Part of India’s appeal lies in expectations of rising domestic demand fueled by an expanding middle class. United Nations data show that the country’s population exceeds the mid-year figure in China and reaches about 1.43 billion people, while it is expected that the gap will only grow.
Investors also expect large multinational corporations to move production from China to India. The American manufacturer of chips Advanced Micro Devices said on Friday that it plans to invest $ 400 million in the country over five years, including in a new design center, which will be the largest in the company.
Money is also flowing into Vietnam, which MSCI considers a “frontier market.” The benchmark VN-Index has jumped by 20% this year.
OVER THE PAST MONTH, EIGHT COUNTRIES HAVE RAISED THE KEY RATE, TWO HAVE LOWERED IT
In July, the actions of regulators in relation to PREP, as well as a month earlier, were somewhat multidirectional.
The cost of borrowing has been raised by Russia, USA, EU, UK, Canada, Denmark, Turkey, Thailand.
Brazil and Chile lowered the rate.
With regard to CPI, the picture is as follows – the indicator is growing in Russia, UK, Chile, Taiwan, Argentina and Turkey. In other states, it is decreasing
INFLATION IN TURKEY: DUE TO THE CENTRAL BANK’S INDECISION, THE PRICE SPIRAL IS UNWINDING MORE AND MORE
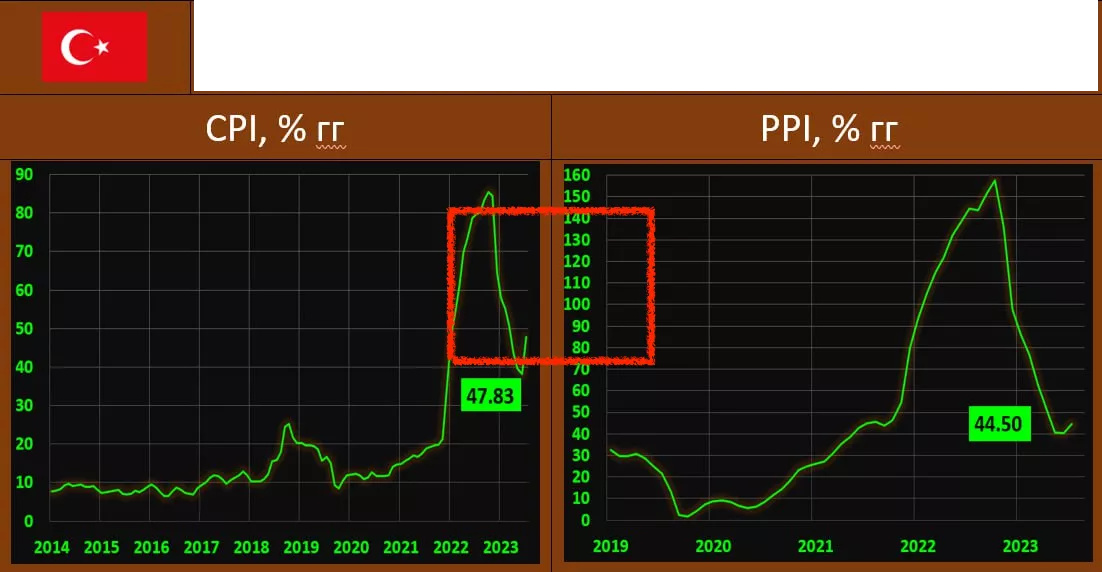
The pace, and especially monthly rates, soared sharply. This is not surprising in view of the extremely cautious behavior of the Central Bank, which has already raised the rate 2 times (17.5%) under the new leadership, but this is extremely insufficient to curb price growth. The Turkish lira is currently trading near historical lows of about 27 USD TRY.
According to the Turkish Statistical Institute, the growth of consumer prices in the country in July amounted to 9.49% mm / 47.83% yy vs 3.92% mm / 38.21% yy in June. The figures are slightly higher than the forecast, waiting for 9.1% mm / 47.3% yy
Rising producer prices: 8.23% mm / 44.5% kg vs 6.5% mm / 40.42% yy a month earlier.
The pace, and especially monthly rates, soared sharply. This is not surprising in view of the extremely cautious behavior of the Central Bank, which has already raised the rate 2 times (17.5%) under the new leadership, but this is extremely insufficient to curb price growth. The Turkish lira is currently trading near historical lows of about 27 USD TRY.
The first 3 days of the fall indicate that the August sale was preliminary. A rally after the July events is preferable
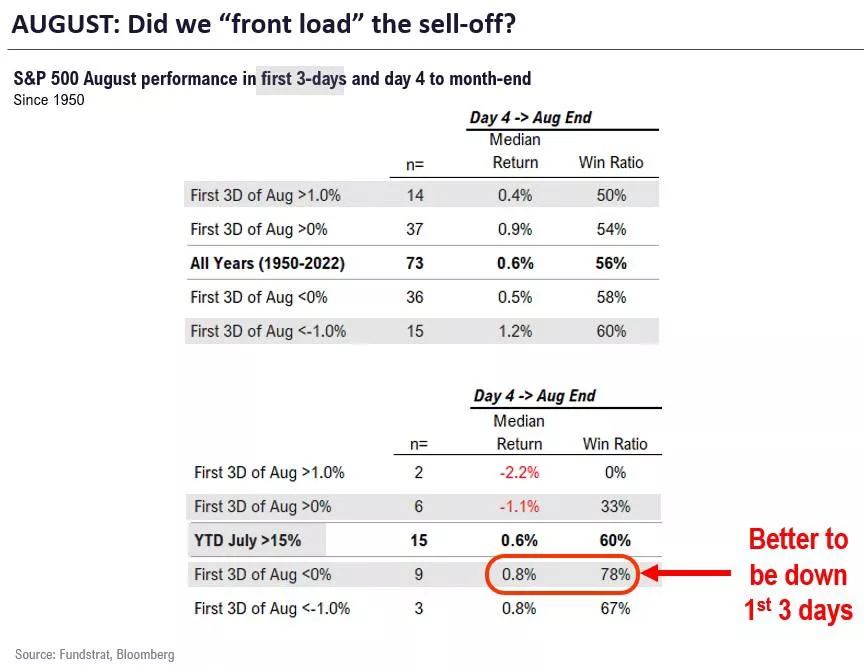
Data analysts have checked whether there is any impact on the profitability of August based on the profitability of the first three days:
•Since 1950, when in August the first 3 days fell >-1%:
– yield from the 4th day to the end of the month +1.2% (60% win ratio)
• Since 1950, when the first 3 days of August increased> 1%:
– yield from the 4th day to the end of the month +0.4% (50% win ratio)
• Since 1950, all years:
– yield from the 4th day to the end of the month +0.6% (56% win ratio)
Thus, it is obvious that the worse the beginning of August (the first 3 days), the better the rest of the month.
When markets have a strong momentum in August (as in 2023), the more intermittent the beginning of August, the better. For the reasons mentioned above, I see that this will happen in 2023. The conclusion is this: I believe that the selling pressure in August is frontal, so the rest of the month is safer for investors. But this does not mean that we should lose caution.
@ESG_Stock_Market